Obtain the Continuity Equation for a Steady Incompressible Flow in Polar
In the previous article, we have discussed the continuity equation in fluid mechanics, from the law of conservation of mass. In this article, we will discuss the continuity equation of fluid-particle in the three-dimensions and also in the Polar coordinates.
Continuity Equation
As we stated the equation based on the law of conservation of mass is called the continuity equation. For a fluid flowing through a pipe at all the cross-sections, the quantity of the fluid per second is constant.
Consider two cross-sections of a pipe as shown in the following figure
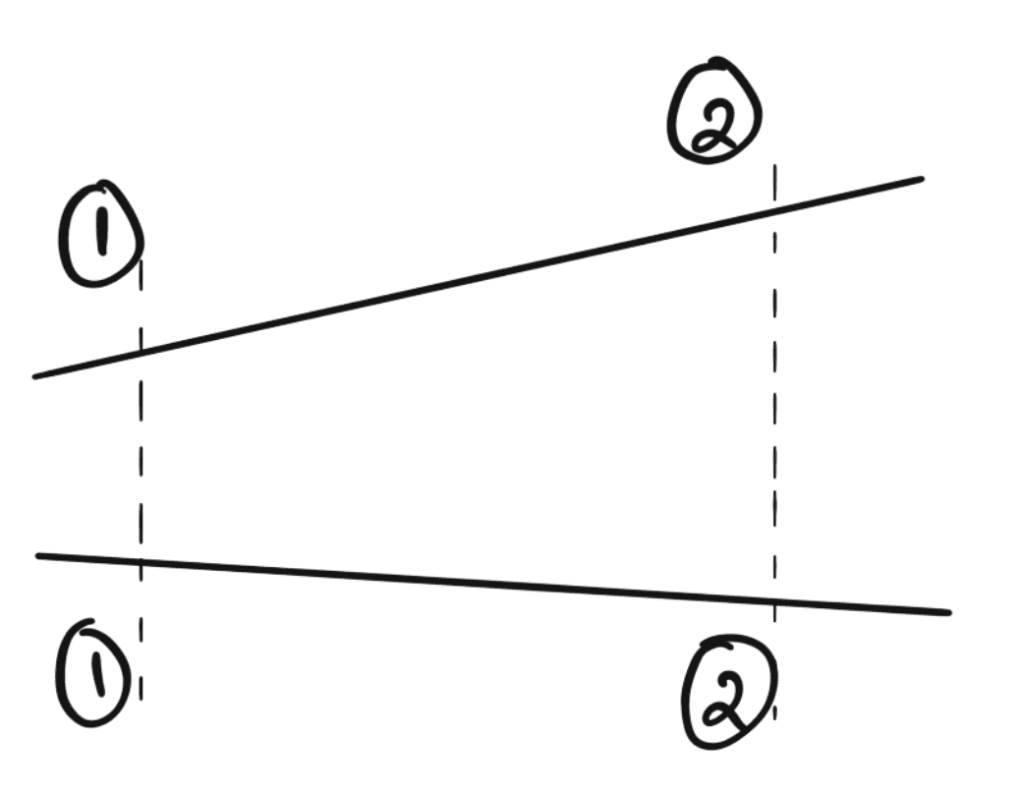
Let
V1 = Average velocity at cross-section 1-1
ρ1 = Density at section 1-1
A1 = Area of pipe at section 1-1
and V2, ρ2 A2, are corresponding values in section, 2-2.
The rate of flow at section 1-1 = ρ1 A1V1
The rate of flow at section 2-2 = ρ2 A2V2
According to the law of conservation of mass from the above
Rate of flow at section 1-1 = Rate of flow at section 2-2
The above equation is applicable to compressible as well as incompressible fluids and is called Continuity Equation.
If the fluid is incompressible, then ρ1 = ρ2, and the above continuity equation reduces as follows
A1V1 = A2V2
* Law of conservation of mass: Law of conservation of mass states that the mass can neither be created nor destroyed but is transformed from one form to another.
Continuity Equation in Three Dimensions
Consider a fluid element of lengths dx, dy and dz in the direction of x, y and z.
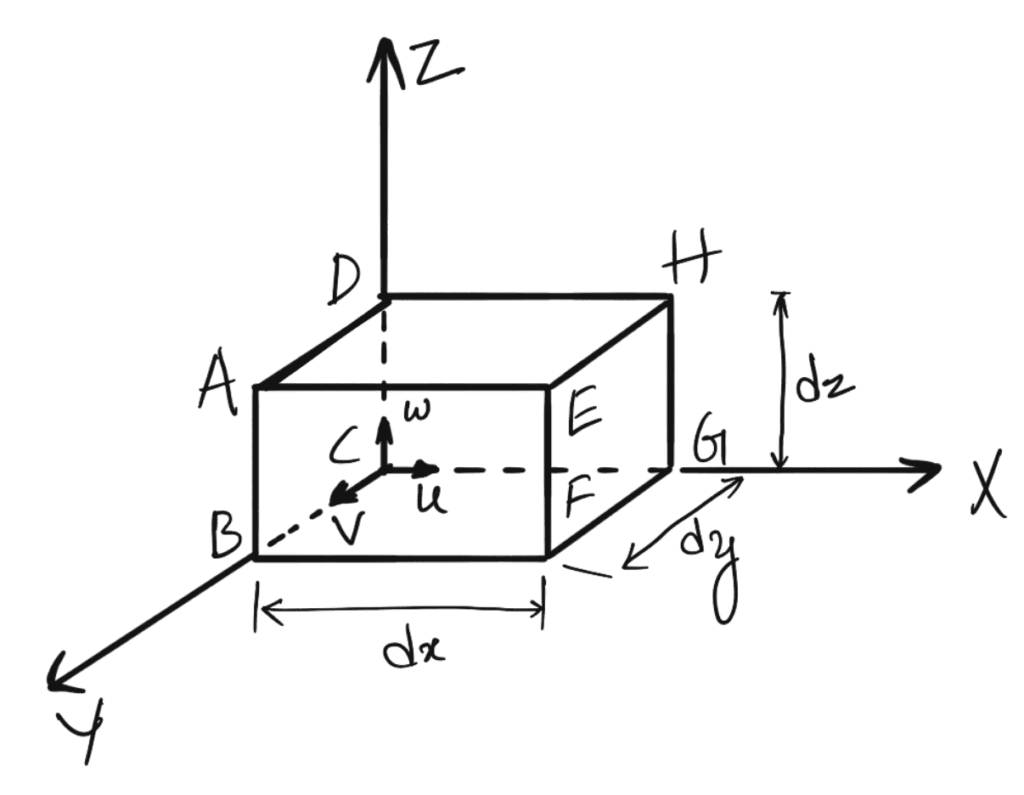
Let u, v and w are the inlet velocity components in x, y and z directions respectively.
Mass of fluid entering the face ABCD per second = ρ × Velocity in x-direction × Area Of ABCD
= ρ × u × (dy × dz)
Then the mass of fluid leaving the face EFGH per second can be written as follows
= ρu × dy dz + ∂/∂x (ρu × dy dz) dx
Gain Of mass in x-direction = Mass through ABCD — Mass through EFGH per second
= (ρu × dy dz) – [(ρu × dy dz) + ∂/∂x (ρu × dy dz) dx]
= – ∂/∂x (ρu × dy dz) dx
= – ∂/∂x (ρu) × dy dz dx
Similarly, the net gain of mass in the y-direction can be written as follows
= – ∂/∂y (ρu) × dy dz dx
Similarly, the net gain of mass in the z-direction also can be written as follows
= – ∂/∂z (ρu) × dy dz dx
The total net gin of masses will be = Sum of the net gain of mass in x-direction y-direction and z-direction
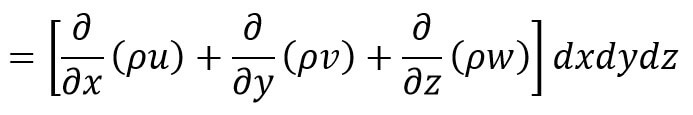
As per the Law of conservation of masses, as mentioned above, the mass is neither created nor destroyed in the fluid element, the net increase of mass per unit time in the fluid element must be to the rate of increase of mass of fluid in the element.
But the mass of fluid in the element is = ρ × dx × dy × dz
The rate of increase of mass with time is = ∂/∂t (ρ × dx × dy × dz)
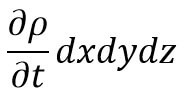
As per the above statement, we can Equate the two expressions of the net increase of mass per unit of time with the rate of increase of mass of fluid in the element, we get
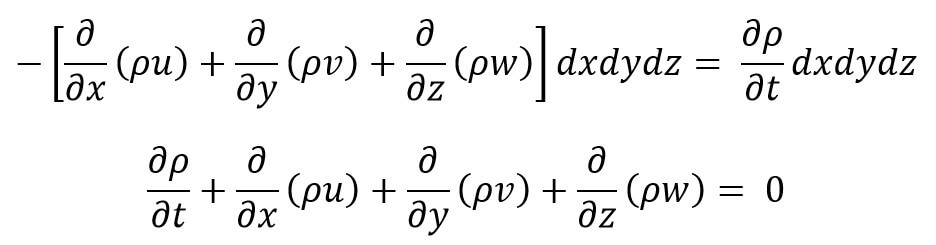
This equation (a) is the continuity equation in cartesian coordinates in its most general form.
This equation is applicable to the following types of flows:
- Steady and unsteady flow
- Uniform and non-uniform now
- Compressible and incompressible fluids
For steady flow, we know ∂ρ/∂t = 0, hence equation (a) becomes as follows
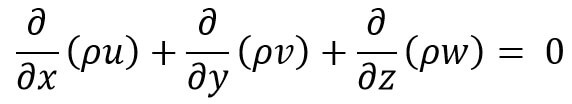
If the fluid is incompressible, then ρ is constant and the above equation (a) becomes as follows
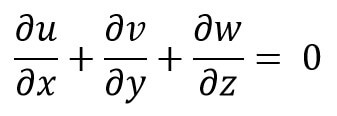
This Equation (b) is the continuity equation in three dimensions.
For a two-dimensional flow, the component w = 0 and hence continuity equation becomes as
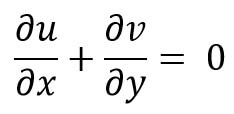
Equation (b) and Equation (c) are the continuity equation in three-dimensions and two-dimensions respectively.
Continuity Equation in Cylindrical Polar Co-ordinates
The Continuity equation in cylindrical polar coordinates (r, θ, z co-ordinates) is derived by the procedure given below.
Let us consider a two-dimensional incompressible flow field.
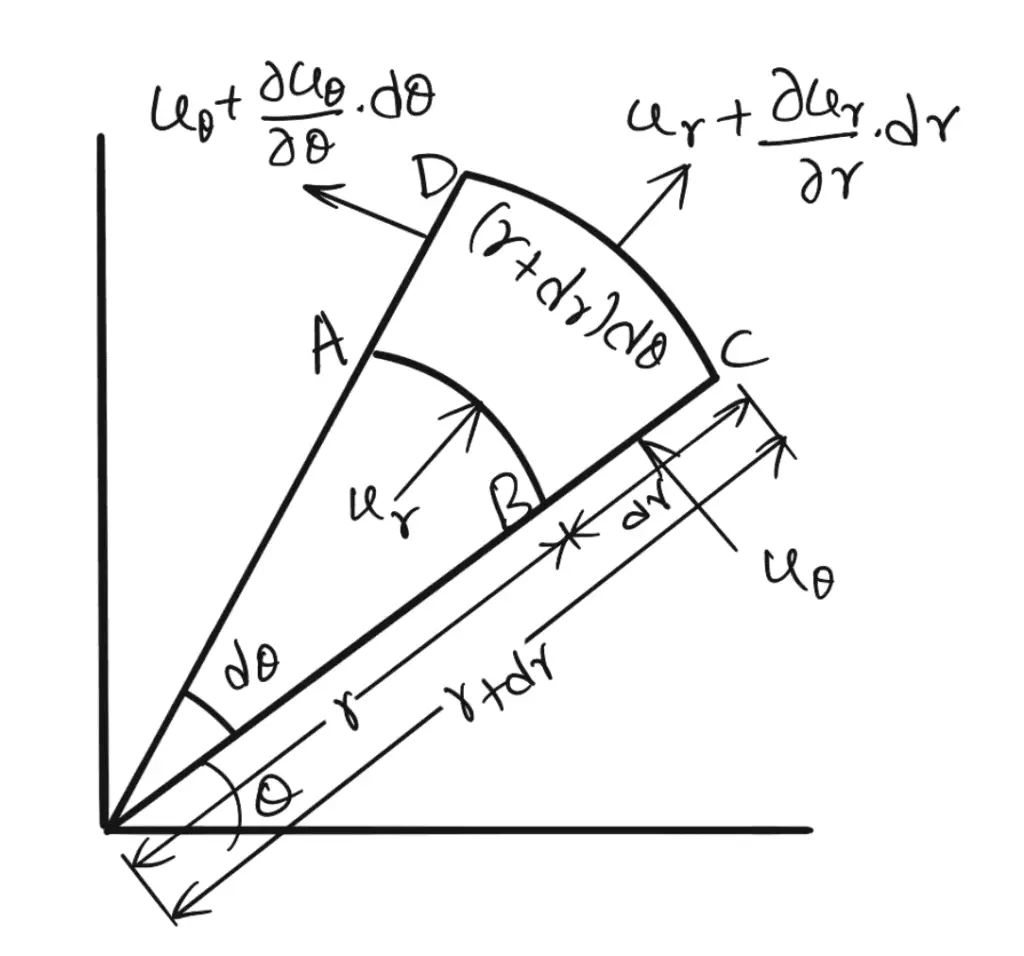
The two-dimensional polar coordinates are r and θ.
Consider a fluid element ABCD between the radii r and r + dr as shown in the above figure
The angle subtended by the element at the centre is dθ.
The components of the velocity V are ur in the radial direction and uθ in the tangential direction.
The sides of the element are having the lengths as follows
Side AB = r dθ
Side BC = dr
Side DC = (r + dr) dθ
Side AD = dr
The thickness of the element perpendicular to the plane of the paper is assumed to be unity.
The fluid flow is in Radial Direction(r- direction)
Now Consider the flow in the radial direction
Mass of fluid entering the face AB per unit time = ρ × Velocity in r-direction × Area
= ρ × ur × (AB × 1)
= ρ × ur × (r dθ × 1)
= ρ ur r dθ
Mass Of fluid leaving the face CD per unit time
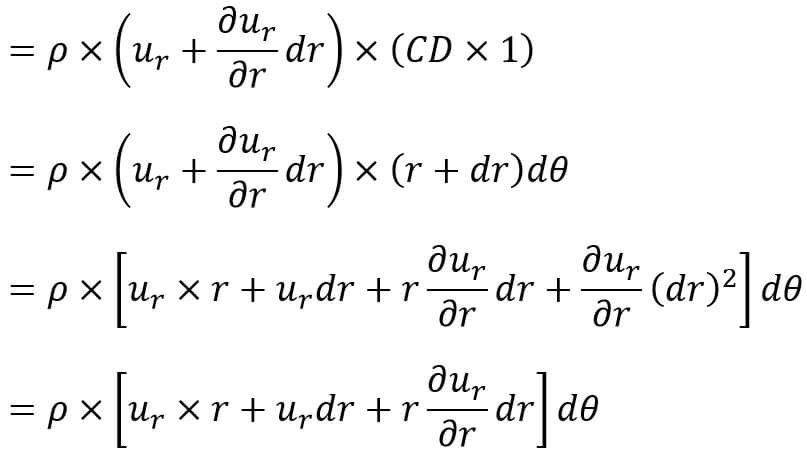
The term containing (dr)2 is very small and has been neglected
Gain of mass in r-direction per unit time
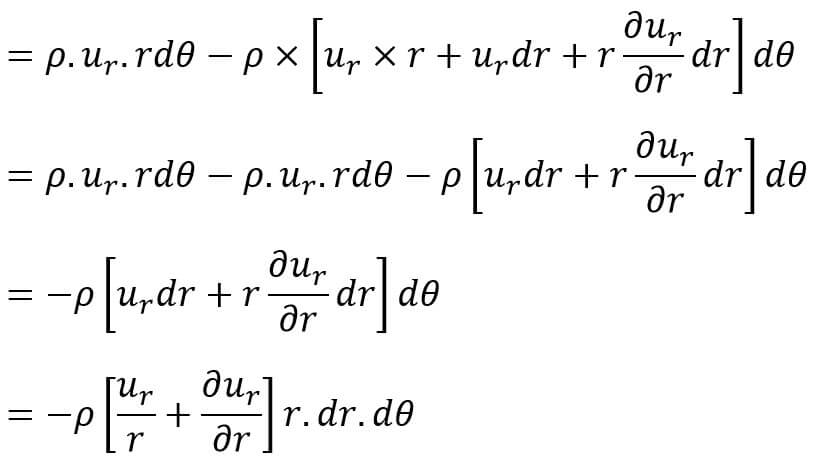
This is written in this form because (r × dθ × dr × 1) is equal to the volume of the element.
The fluid flow is in θ-Direction
let us now consider the fluid flow is in θ-Direction
Gain in mass in θ-direction per unit time = (Mass through BC – Mass through AD) per unit time
= [ρ × Velocity through BC × Area – ρ × Velocity through AD × Area]
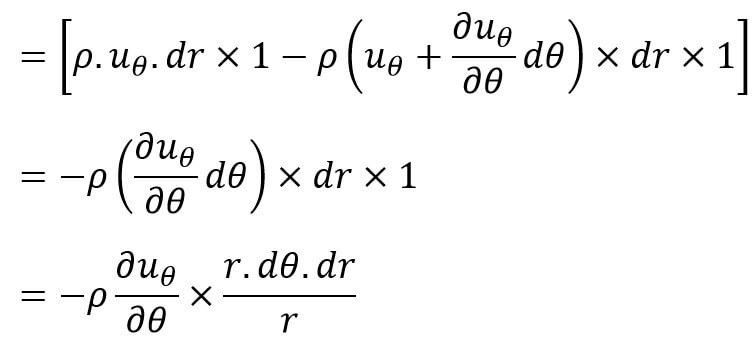
The total gain in fluid mass per unit time
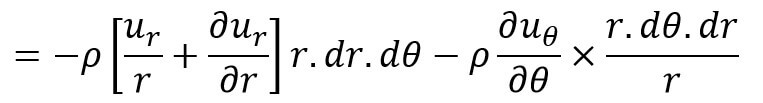
But the mass of the fluid element = ρ × Volume of the fluid element
= ρ × [rdθ × dr × 1]
= ρ × rdθ × dr
The rate of increase of fluid mass in the element with time
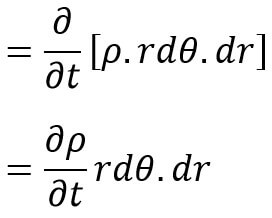
( ∴ (rdθ × dr × 1) is the volume of element and is a constant quantity)
From the Law of Conservation of mass, the mass is neither created nor destroyed in the fluid element, hence net gain of mass per unit time in the fluid element must be equal to the rate of increase of mass Of fluid in the element.
Hence equating the two expressions given by equations (d) and (e), we get
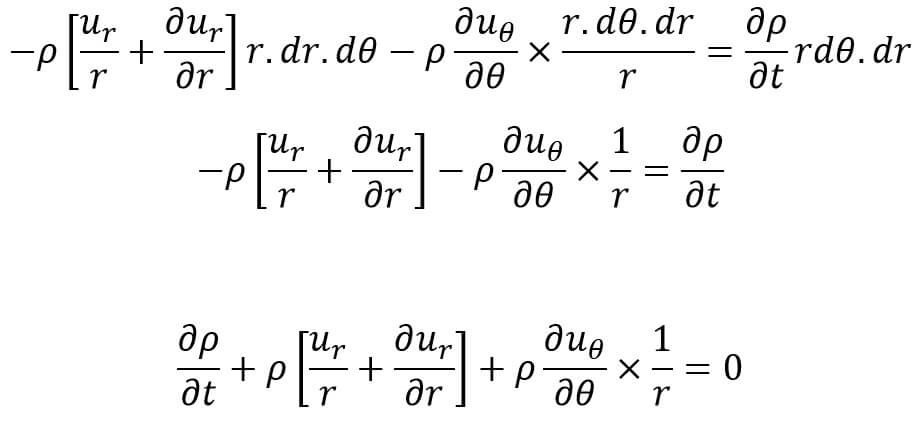
This equation (f) is the Continuity Equation in Cylindrical Polar Co-ordinates for a two-dimensional flow.
For steady-state flow, we know ∂ρ/∂t = 0, hence equation (f) becomes as follows
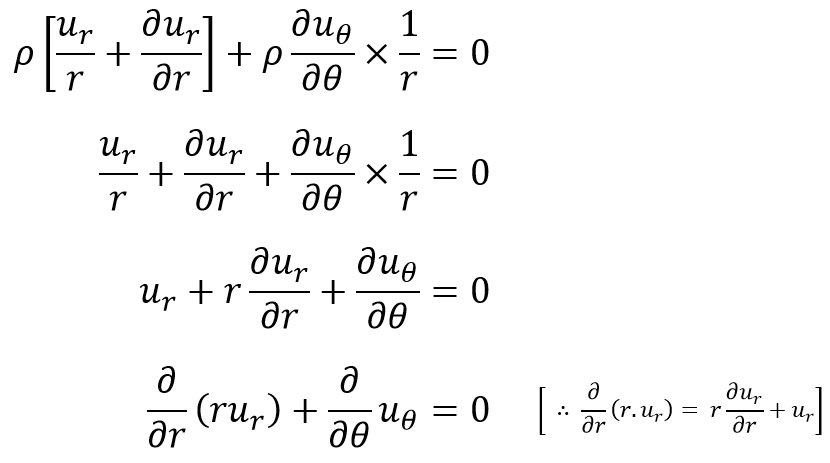
This equation (g) represents the continuity equation in polar coordinates for two-dimensional steady incompressible flow.
Example problems on Continuity Equation
Let us solve an example problem to determine whether any given velocity equation represents a possible physical fluid.
Problem Statement: Verify whether the following velocity components represent the physically possible flow.
ur = r sin θ, uθ = 2r cos θ
Answer:
Given data
ur = r sin θ
uθ = 2r cos θ
For a physically possible flow, the continuity equation,
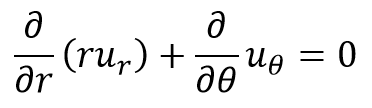
should be satisfied
ur = r sin θ
Multiplying the above equations by r we get
rur = r2 sin θ
Let us differentiate the above equation with respect to r we get
∂/∂r (rur) = ∂/∂r (r2 sin θ)
∂/∂r (rur) = 2r sin θ
uθ = 2r cos θ
Let us differentiate the above equation with respect to r we get
∂/∂r (uθ) = ∂/∂r (2r cos θ)
∂/∂r (uθ) = – 2r sin θ
Summing the above two equations we get
∂/∂r (rur) + ∂/∂r (uθ) = 2r sin θ – 2r sin θ = 0
Hence the continuity equation is satisfied.
Hence the given velocity components represent a physically possible flow.
Let us know if you have any doubts in this regard in the comment section below.
Source: https://extrudesign.com/what-is-continuity-equation-in-three-dimensions-and-polar-coordinates/
0 Response to "Obtain the Continuity Equation for a Steady Incompressible Flow in Polar"
Post a Comment